
- 🦖Introduction | What This Content Will Help You Figure Out
- 📝Chapter 1 | What Kind of Permits Do You Need to Keep a Tyrannosaurus?
- 🏠Chapter 2|Can You Really Keep a T-Rex Indoors? Required Space & Structural Conditions
- 📏First, Let’s Reconfirm the Size of a T-Rex
- 🏟️You’d Need at Least a Gymnasium-Sized Area
- 🧱The Floor Must Support 10 Tons—Non-Negotiable
- 🏢Keeping One in an Apartment Is Nearly Impossible
- 🏞️If You’re Going to Keep One, Rural or Underground Facilities Are Most Realistic
- 🧠A Few Thoughtful Touches Could Improve Comfort
- 📝Summary|A T-Rex Is Something You “House,” Not Just “Keep”
- 🍖Chapter 3|An Outrageous Appetite! How Much Does It Cost to Feed a T-Rex?
- 🚽Chapter 4|The T-Rex “Poop Problem” and How to Handle It
- 🗣️Chapter 5|Training, Noise Control, and Preventing Neighborhood Trouble with a T-Rex
- 🩺Chapter 6|Medical Care, Insurance, and Old Age for a Tyrannosaurus
- 🏥Does a T-Rex Even Have a “Primary Care Veterinarian”?
- 🧬A Dedicated T-Rex Medical Research Center Would Be Essential
- 💉Vaccines, Infections, and Preventive Healthcare
- 🛡️Can a T-Rex Get Insurance?
- 👴T-Rex Lifespan and Senior Care
- 🛏️Designing a Comfortable Senior Life
- ⚰️When a T-Rex Dies—Handling the Final Stage
- 📝Summary|The Final Chapter of Responsibility
- 🆘Chapter 7|What If a Disaster Strikes? Emergency & Disaster Preparedness for Living With a T-Rex
- 🌪️1. If an Earthquake Strikes—What Happens to the T-Rex?
- 🧷2. The Priority Is Not “Evacuation”—But “Containment”
- 🔌3. Power Outages—Your Lifeline in Crisis
- 💧4. Flooding & Water Damage—The Risk of “Buoyancy”
- 📦5. Emergency Supplies Must Be “Dinosaur-Scale”
- 📡6. Coordination With Authorities & Neighbors Saves Lives
- 📝Summary|Living With a T-Rex Requires Serious “Disaster Readiness”
- 🆘Chapter 7 | What If a Disaster Strikes? Disaster Preparedness for a Home Living With a Tyrannosaurus
- 🌪️1. What Happens to a T. rex During an Earthquake?
- 🧷2. In a Disaster, the Goal Is Not “Evacuation” but “Isolation”
- 🔌3. Power Outages Become a Life-or-Death Situation
- 💧4. The Hidden “Buoyancy Risk” in Flooding
- 📦5. Emergency Stockpiles Must Be “Mega-Scale”
- 📡6. Coordination With Neighbors Can Save Lives
- 📝Summary | Living With a T. rex Requires Disaster-Readiness
- 🎡Chapter 8 | Daily Life and Leisure With a Tyrannosaurus
- 💰Chapter 9 | How Much Does It Cost to Keep a T. rex for a Year? A Complete Breakdown of Realistic Care Expenses
- 🕊Chapter 10 | What If Your Tyrannosaurus Reaches the End of Its Life? Facing Farewell and What Comes After
- 🦖How Long Does a Tyrannosaurus Live?
- 📉How Does Aging Appear?
- 🛏What Preparations Are Needed for Caregiving and End-of-Life Support?
- 💐When the Time Comes—How to Say Goodbye
- 🌱Life After Loss and the “Hole in the Heart”
- 📚Passing the T. rex’s Story to Future Generations
- 📝Summary | What It Means to Be Responsible for a Life
- 📘Final Summary | The Unexpected Truths Revealed by Seriously Imagining an “Impossible Fantasy” of Keeping a T. rex
🦖Introduction | What This Content Will Help You Figure Out
This content is for those who want to seriously simulate, from a realistic perspective, what it would actually be like if you could keep a Tyrannosaurus indoors.
Recommended for people like this 👇
-
People who want “intellectual entertainment” that makes for a great conversation starter with kids or friends
-
People who want to post “meme × serious” style content that can go viral on note or social media
-
People who want to take something that “sounds like pure fiction” and ground it in realistic detail
For those people, this content will thoroughly examine everything from laws, space, feed costs, excretion, training, medical care, to disaster preparedness, and explain in an easy-to-understand way, from an “indoor keeping” perspective, how far it could realistically be possible.
🟥Can You Actually Keep a T-Rex?
“Could you really keep a Tyrannosaurus as a pet?”
It’s that boundary between imagination and reality everyone has wondered about at least once.
But online, most of what you find is pure fantasy or vague jokes.
Very rarely do you see it discussed from the angle of “What if we seriously tried to live with one?”
🟧Try Imagining It
What if there were a 12-meter-long carnivorous dinosaur in the living room of your detached house?
-
How loud would its roar be?
-
What would you feed it?
-
How would it go to the bathroom?
-
What about medical care?
-
What if an earthquake hit?
-
What if there were a power outage?
-
What if it escaped…?
What sounds like a dream could instantly turn into a living hell.
We can’t talk about this anymore while ignoring the “reality of keeping such a creature.”
🟩Let’s Start a Serious Simulation
That’s why, in this content, we’ll seriously simulate keeping a Tyrannosaurus as an “indoor pet” and cover:
-
How much space you’d need
-
Laws and facilities
-
Feed costs and training
-
Medical care and insurance
-
Disaster preparedness and even its old age
We’ll dig into everything with the level of detail you’d expect from a pet care manual, but from a realistic perspective.
🟦Who This Is Especially For
-
People who want to go viral on note or social media with “meme × realistic” content
-
Curious-minded people who want to spice up conversations with their kids or family
-
Adults who love Tyrannosaurus so much they’ve started to actually want to keep one
🟨All Right, Let’s Begin
If you were really going to live with a T-Rex, what would it be like?
From here on, you’ll step into that “virtual life with a dinosaur.”
▼
So now, let’s start with
Chapter 1: “What Kind of Permits Do You Need to Keep a Tyrannosaurus?”
📝Chapter 1 | What Kind of Permits Do You Need to Keep a Tyrannosaurus?

If you ever thought, “I want to keep a Tyrannosaurus indoors,” the very first wall you’d hit is the issue of legal “permits” and “keeping environment.”
Even when you own a dog or a cat, depending on the region, you may need to file notifications or have them vaccinated.
So if you were seriously going to keep a massive carnivorous dinosaur over 12 meters long, it would clearly no longer be considered a typical “pet” and would almost certainly be treated as a “specially regulated dangerous animal.”
In this chapter, we’ll explain in realistic and easy-to-understand terms what kinds of permits and procedures you’d need to keep a Tyrannosaurus.
🛑First of All: It Would Count as a “Designated Dangerous Animal”
If a Tyrannosaurus were somehow brought back to life in the modern era, it would undoubtedly be designated as a “dangerous animal subject to special regulation.”
“Dangerous animals” in this context are animals designated by the government as having the potential to cause harm to humans. Currently this category includes tigers, bears, crocodiles, and so on.
The purpose of this system is to “minimize the impact on human life and the environment in the event of an escape.”
A Tyrannosaurus would weigh around 7–10 tons, be able to run at over 40 km/h, and take down prey with its huge jaws.
Clearly, it would be a serious threat to humans, so the act of “keeping one” itself would definitely be subject to strict legal restrictions.
📝Main Procedures You’d Need
✅ 1. Applying for a “Dangerous Animal Keeping Permit” to Your Prefecture
In Japan, if you want to keep a designated dangerous animal, you must obtain permission from the governor of the prefecture.
This is based on the Act on Welfare and Management of Animals, and violations can reportedly result in up to one year in prison or a fine of up to about $6,400 (instead of ¥1,000,000).
The main things required for this procedure would be:
-
Identification and background information of the keeper
-
Detailed blueprints of the planned keeping facility
-
Design documents showing how the facility will prevent the animal from escaping
-
Information about the distance from surrounding areas (schools, residential zones, etc.)
At this point, you can probably already tell that the bar is extremely high.
✅ 2. Designing and Getting Approval for a Dedicated, Extremely Strong Facility
If you’re going to keep a Tyrannosaurus, you’ll need a dedicated keeping facility.
Imagine this: if your T-Rex casually head-butted a wall on a whim… normal concrete wouldn’t stand a chance.
So the facility would need at least the following conditions:
-
Reinforced concrete construction (with a recommended thickness of at least 50 cm)
-
Anti-escape measures from all directions, including the ceiling and doors
-
Soundproofing to deal with its roaring
-
Double-door systems and protective barriers so that no one except the keeper can approach it carelessly
On top of that, on-site inspections by local government staff and certified animal handlers would also be required, so passing on paperwork alone would not be realistic.
🧬Ethical Issues: Handling an “Extinct Species”
There’s another major challenge.
A Tyrannosaurus is, by definition, an extinct animal.
If, hypothetically, the latest scientific technology (like genetic engineering or cloning) allowed us to bring back a Tyrannosaurus, then from that moment on, humanity would have the power to revive extinct species.
At that point, things like the “Act on Conservation of Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora” and the “Convention on Biological Diversity” would come into play.
More concretely, questions like these would arise:
-
Does ownership of such a resurrected animal even make sense?
-
Is it acceptable to treat an extinct species as a “product” to be bought and sold?
-
Can we really call a cloned individual “natural”?
-
How would we control the population if it could reproduce?
All of these lie in a very delicate zone where science, ethics, and law intersect.
⚖️“Freedom to Keep” vs. “Responsibility to Protect”
Keeping a pet is not just about “having fun.”
It means facing a living being and taking responsibility for it until the very end.
Keeping a large, dangerous animal like a Tyrannosaurus is not just your personal issue—it’s an action that affects society as a whole.
Because, in the worst case, other people could be dragged into the consequences, permits, facilities, and ethical aspects are all strictly questioned.
So if you have the desire to “keep one,” you also need to deeply consider your simultaneous “responsibility to protect.”
📝Summary | The First Step to Living with a T-Rex Is “Resolve”
By now, you’ve probably realized this already:
keeping a Tyrannosaurus would require enormous preparation and multiple layers of permits.
To summarize the key points 👇
-
A T-Rex would be designated as a “dangerous animal,” and you’d need a permit from your prefectural government to keep one.
-
You’d need an extremely sturdy keeping facility, double safety systems, and consideration for your neighbors.
-
Handling an extinct species also means dealing with ethical issues and international regulations.
In other words, from the moment you think “I want to keep one,”
you also need the “resolve to take responsibility for that life” and the “resolve to coexist with society.”
That said, if after reading all this you still feel,
“I still want to keep one!”—then maybe you do have what it takes to move on to the next step.
In the next chapter, we’ll dig into just how much space and what kind of structure you would actually need to keep a Tyrannosaurus indoors, in realistic detail.
Stay tuned.
🏠Chapter 2|Can You Really Keep a T-Rex Indoors? Required Space & Structural Conditions

In the previous chapter, we discussed the “permits required to keep a Tyrannosaurus.”
But even if you clear the legal hurdles, that alone does not mean you can simply bring one home.
The next problem is “space” and “structure.”
A T-Rex is not a small dog that will curl up on your lap, after all.
In this chapter, we’ll explore whether it’s realistically possible to keep a Tyrannosaurus indoors, what kind of space is required, and what structural conditions your home would need.
📏First, Let’s Reconfirm the Size of a T-Rex
Before anything else, let’s review the basic size of a Tyrannosaurus.
-
Total length: approx. 12 meters (about the length of two buses)
-
Height: approx. 4 meters (equivalent to a 2-story house)
-
Weight: estimated 7–10 tons (equal to two African elephants)
In other words, to welcome one into your home, you’d need space with the size and strength to let “two elephants run around safely.”
You may already feel that an ordinary home won’t stand a chance.
🏟️You’d Need at Least a Gymnasium-Sized Area
So how much space does a T-Rex need to live comfortably?
In general, an animal’s enclosure should be “3 times the body length × 2 times the body height.”
Applying this standard to a Tyrannosaurus gives us:
-
Minimum required space: approx. 40m (length) × 20m (width) × 10m (height)
-
In reality, more space is preferable to include exercise areas, feeding zones, and resting zones
This size is roughly comparable to the gymnasium of a typical elementary or middle school.
And because “indoor keeping” requires a fully enclosed roofed structure, simply renting a gymnasium still wouldn’t be structurally sufficient.
🧱The Floor Must Support 10 Tons—Non-Negotiable
Even if you secure the space, the next critical factor is floor strength.
A T-Rex weighs about 10 tons—equivalent to 10 passenger cars.
Even though that weight is distributed across four legs, the pressure per point is enormous.
For reference, a typical residential floor can only withstand around 180 kg/m².
Meanwhile, the load concentrated under a T-Rex’s foot would be several tons, meaning:
-
Normal wooden homes → Completely impossible
-
Standard reinforced concrete apartments → Unsafe
-
Industrial warehouse-strength flooring → Potentially feasible
In other words, to keep one indoors, the entire floor structure must be redesigned from scratch.
If building from the ground up, a reinforced structure directly supported by the foundation would be ideal.
🏢Keeping One in an Apartment Is Nearly Impossible
After reading this far, you may already be thinking, “There’s no way I can keep one in my apartment…”
And yes, keeping a T-Rex in a normal apartment is essentially impossible.
Here are a few reasons why:
● It Won’t Fit Through the Elevator
A 4-meter-tall T-Rex can’t even fit through most apartment entrances.
In many cases, it would get stuck at the front door.
● The Noise and Vibrations Would Be Catastrophic
Each step would shake the floors, sending vibrations to every neighboring unit.
A few soundproof mats won’t fix that.
● It Would Violate Most Building Regulations
Many apartment rules restrict which animals you can keep.
Even buildings that allow small dogs would certainly not include a Tyrannosaurus.
🏞️If You’re Going to Keep One, Rural or Underground Facilities Are Most Realistic
So where could you realistically live with a Tyrannosaurus?
The two most practical options would be:
✅ 1. Build a Dedicated Facility on a Large Rural Property
-
Buy land deep in the mountains or countryside and build your own enclosure
-
You won’t need to worry about noise, odor, or waste disturbing neighbors
-
If you meet building codes and animal welfare laws, obtaining permits may be possible
This is essentially a “private zoo lifestyle.”
✅ 2. Create a Dedicated Underground Habitat
-
Noise and vibrations can be minimized
-
Can offer a degree of safety even in disasters
-
However, construction costs may reach astronomical levels
Either way, keeping a T-Rex is less “indoor pet ownership” and more “operating a managed facility.”
🧠A Few Thoughtful Touches Could Improve Comfort
Still, having a large space is not everything.
T-Rexes likely had “preferences” and “comfort needs” as well.
For example:
-
Install skylights to allow natural sunlight
-
Use slightly softer flooring material to reduce joint strain
-
Create shaded, enclosed rest areas
Small touches like these could greatly reduce the stress levels of your T-Rex—something humans can relate to as well.
📝Summary|A T-Rex Is Something You “House,” Not Just “Keep”
Let’s summarize today’s key points 👇
-
Keeping a T-Rex indoors requires at least gymnasium-level space
-
Floors must support 10-ton levels of weight to avoid collapse
-
Keeping one in an apartment or standard house is essentially impossible
-
If you want to keep one, rural land or underground facilities are the only realistic options
A T-Rex is not a “pet,” but rather a “large lifeform you coexist with.”
It’s less about bringing one into a human home and more about “building a home for the dinosaur itself.”
In the next chapter, we’ll explore how much food a T-Rex needs each day and what the cost would be.
“How much does it eat per day?”
If you’re curious, be sure to check out the next chapter.
🍖Chapter 3|An Outrageous Appetite! How Much Does It Cost to Feed a T-Rex?

The grand dream of keeping a Tyrannosaurus indoors.
We’ve covered the legal issues, the structural requirements, and the sheer amount of space needed—but now we arrive at today’s theme: “Food.”
Yes—the food budget.
When keeping any pet, one thing you cannot avoid is feeding it every single day.
But the creature in question is the colossal carnivorous dinosaur, Tyrannosaurus.
You can’t just pour some kibble into a bowl like you would for a Shiba Inu.
How much does it actually eat?
And how much would feeding it cost?
Let’s dive into the black-hole-like appetite of the T-Rex.
🍖How Much Does a T-Rex Eat in a Day?
First, let’s review the basics.
A Tyrannosaurus is estimated to weigh between 7 and 10 tons—
roughly the weight of two African elephants.
To maintain such massive body mass, it obviously needs a tremendous amount of nutrients.
So, how much would it actually eat?
-
General estimates suggest 20–30 kg of meat per day
-
Over one week, that’s equivalent to one full cow’s worth of meat
That number alone defies all common sense.
If you tried storing its food in a household fridge—
it wouldn’t even hold a single day’s worth.
💵How Much Would It Cost Per Month?
Let’s get into the real numbers: how much money are we talking about?
Meat prices vary greatly depending on the type and sourcing.
Here, we’ll calculate using “bulk, non-premium meat intended for large-scale livestock feeding”—not human-grade cuts.
【Daily Feeding Cost Estimate】
-
Mixed ground beef/pork/chicken (wholesale): approx. ¥500/kg → about $3.20/kg
-
20 kg per day → approx. $64/day
-
30 kg per day → approx. $96/day
【Monthly Feeding Cost】
-
At minimum: $1,900–$2,900/month
-
Including meat price fluctuations & nutrition adjustments →
$3,200+/month is very possible
This does not include costs for food preparation, storage, or transportation.
Meaning: feeding a T-Rex requires a financial commitment equivalent to a luxury-car loan—every month.
🛒How Do You Even Obtain That Much Food?
Supplying 20–30 kg of fresh meat every single day is a challenge in itself.
✅ 1. Wholesale Frozen Meat Suppliers
The most realistic option is sourcing from commercial frozen-meat wholesalers.
-
Suppliers that sell to supermarkets and restaurants
-
Wide availability: ground meat, bone-in cuts, organ meats
-
Bulk purchases are possible, cost performance is stable
For a T-Rex, quantity and nutrition matter more than “flavor.”
Rougher cuts with bones and organs may actually be closer to what it ate in nature.
However, storage and sanitation become major problems.
A T-Rex diet requires industrial-level handling capacity.
You will almost certainly need large commercial freezers or cold-storage rooms.
✅ 2. Partnering With Local Farms or Ranches
Another option is to contract directly with livestock farms.
-
You can source whole cows, pigs, or chickens
-
If you butcher them yourself, costs decrease
-
A recurring contract ensures steady supply
But this requires butchering skills and proper processing facilities.
There are also legal risks if you violate livestock, hygiene, or food-handling regulations.
🧼Sanitation Is Critical for a T-Rex’s Diet
T-Rexes were strictly carnivorous.
If the meat is spoiled or contaminated, it can easily lead to digestive problems or illness.
Maintaining such a massive creature requires a surprisingly delicate feeding environment.
For example:
-
Provide fresh food daily
-
Thaw/prepare meat in sanitary conditions
-
Disinfect feeding tools and dishes every day
-
Immediately remove leftover scraps after meals
Failing to do this could result in foul odors, harmful bacteria, and pest infestations.
Poor sanitation could also cause conflict with neighbors.
So, maintaining hygiene is far more important than you might think.
👛Other Hidden Costs
Feeding isn’t the only expense. You may also need to pay for:
-
Electricity for large-scale freezer storage (very high)
-
Labor costs for thawing, preparing, and feeding
-
Vehicles or transport fees for hauling large quantities of meat
-
Infection testing & veterinary costs in emergencies
In short, you’re not just paying for food—
you’re paying for the entire infrastructure that allows the animal to eat safely.
This is far beyond the level of “keeping a pet.”
It’s closer to operating a small ranch or wildlife facility.
📝Summary|A T-Rex’s Food Budget Is a Test of Your Resolve
Thank you for reading.
This chapter covered the realistic costs and logistics of feeding a Tyrannosaurus.
Let’s summarize 👇
-
A T-Rex needs 20–30 kg of raw meat per day
-
Food costs can exceed $3,200 per month
-
Major sourcing routes: wholesalers or direct farm contracts
-
Sanitation, storage, and transport add major extra costs
-
Your ability to “provide food” is a measure of your commitment as a keeper
In other words, keeping a T-Rex means
“preparing the equivalent of one cow’s worth of meat every week.”
Yet the chance to witness such a magnificent creature striding proudly before your eyes…
Some may find the struggle worth the romance.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore another massive challenge:
T-Rex poop—and how to handle it.
Every living thing that eats must also “produce waste.”
But how big of a problem is T-Rex waste?
Stay tuned!
🚽Chapter 4|The T-Rex “Poop Problem” and How to Handle It

When people first hear about keeping a Tyrannosaurus at home, most are shocked by its size or feeding costs.
But in reality, there is an issue just as serious—or even more serious: the problem of waste (poop).
“If it eats, it poops.”
This is a fundamental biological truth for all living beings.
As explained in the previous chapter, a T-Rex eats 20–30 kg of raw meat per day.
Naturally, what comes out is also substantial.
In this chapter, we’ll break down how much waste a T-Rex produces, how to manage it,
and what responsibilities the owner must be prepared for.
🚽So… How Much Does It “Produce” Daily?
To make things easier to imagine, let’s look at the numbers.
A T-Rex consumes 20–30 kg of meat per day.
Carnivores typically excrete about 15–25% of what they eat.
Meaning the daily “output” of a T-Rex is…
-
Approximately 4–8 kg of solid waste per day
-
Plus a large volume of urine
And this is the minimum.
Fat content, organ consumption, and water intake can increase these amounts.
And remember—this is per day.
Over a week: 30–50 kg.
Over a month: 100+ kg of poop to manage.
🚽Equivalent to 10 Human Toilets!? Understanding the Weight
Numbers can be abstract, so let’s compare with something familiar—human toilets.
-
Average adult male daily feces → around 150–200g
-
A T-Rex’s average daily waste (approx. 6 kg) equals…
→ the daily toilet usage of 30–40 people
That’s basically “10 household toilets running at full capacity all day.”
Clearly, this is way beyond what a normal home can handle.
🏗️You’ll Need a Dedicated Waste-Processing Room
Any home keeping a T-Rex must have a dedicated excrement-processing facility.
Pet sheets or litter boxes are impossible—
just one round of T-Rex poop weighs multiple trash bags’ worth.
Realistically, a system like the one below is required 👇
✅ 1. A Dedicated Toilet Room
-
Slightly sloped flooring to guide waste naturally
-
Flush-style drainage system leading to a processing tank
-
Concrete, antibacterial, odor-resistant flooring
-
A sealable room to contain odors
You may even need to “toilet-train” your T-Rex to use the space consistently.
✅ 2. A Vacuum Waste-Collecting System
For animals of this scale, you’ll need a system similar to those used in industrial livestock barns.
-
Built-in suction ports collect waste instantly
-
Waste is stored in a holding tank for later disposal
-
Automatic cleaning to maintain sanitary conditions
Installing such a system at home requires major construction—but skipping it is a severe hygiene risk.
🤢Odor, Infection, and Pest Control Are Mandatory
One cannot ignore the “secondary risks” of T-Rex waste.
These include:
● Odor Issues
Raw meat diets produce incredibly strong-smelling waste.
And because a T-Rex is so large, the odor volume is also overwhelming.
This can easily become a major neighborhood nuisance.
Necessary countermeasures:
-
Powerful ventilation + air purification systems
-
Odor-absorbing filters
-
A sealed toilet-room structure
● Infection Risk
T-Rexes may carry unknown bacteria or parasites.
Even if cloned or revived, they require precautions similar to wild animals.
-
Regular fecal tests
-
Protective gear for waste-handling staff
-
Complete separation of living and keeping areas
This is no longer “pet care.”
It is closer to “wildlife facility management.”
● Pest Infestations
If waste is not dealt with quickly, flies, cockroaches, and even rats can multiply rapidly.
In summer, heat and odor create ideal breeding conditions.
Pest outbreaks can lead to infections and equipment damage.
In short, neglecting T-Rex poop can become life-threatening.
👷A Practical Waste-Management Plan
Realistically, effective T-Rex waste management comes down to three key steps:
-
Train it to eliminate in a designated area
-
Install a system for rapid collection & isolation
-
Ensure airtight containment & scheduled disposal
Managing all of this requires far more than one person.
You’ll likely need dedicated caretakers, cleaners, and formal procedures.
📝Summary|To “Keep” a T-Rex Is to Take Responsibility for Its Waste
How was this deep dive into the T-Rex waste problem?
Let’s summarize 👇
-
A T-Rex produces several kilograms of poop and large amounts of urine daily
-
You need the equivalent capacity of 10 household toilets
-
Dedicated waste rooms and vacuum systems are mandatory
-
Odor, disease, and pest control are life-protecting necessities
-
“Cute” or “cool” is nowhere near enough to handle this responsibility
To keep an animal is to accept everything it outputs—
and with a T-Rex, that responsibility is monumental.
But if you understand all of this and still think, “I want to live with a T-Rex,”
then that determination may truly be the real deal.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore another major challenge:
training, noise control, and preventing neighborhood disputes.
“What if it roars?” “What if it rampages?”
We’ll answer those questions next. Stay tuned!
🗣️Chapter 5|Training, Noise Control, and Preventing Neighborhood Trouble with a T-Rex

When you imagine keeping a Tyrannosaurus indoors—a truly unprecedented lifestyle—one of the first concerns that comes to mind is “training.”
What about its vocalizations?
Will it get violent?
What if the neighbors complain?
And if it panics and runs wild…?
In this chapter, we’ll break down the essential strategies for training, noise control, and avoiding interpersonal or neighborhood conflicts when living with a T-Rex—explained as concretely as possible.
🗯️Is a T-Rex Actually Loud?
One of the biggest questions is the issue of “vocalization.”
Movies often depict T-Rexes roaring with an ear-splitting “GROOAAAAAAR!!”
But in reality, would a real T-Rex sound like that?
Modern research doesn’t have a definitive answer yet.
However, many studies suggest the following possibilities👇
-
Their vocal structures were likely closer to birds and reptiles
-
Their vocalizations were probably not “roars” but low rumbles or resonant vibrations
-
Some theories suggest they produced infrasonic sounds (too low for humans to hear, but strong enough to vibrate air and ground)
In other words, instead of ear-shattering roars, a T-Rex’s sound was likely more like a low, ground-shaking vibration.
Even if not loud to human ears, the vibrations and air pressure could affect surrounding buildings and people.
📣How to Handle the Noise Issue
Even if low-frequency, imagine your T-Rex making a daily “Grrrrr…” each morning—enough to rattle your neighbor’s cupboards.
This makes extensive soundproofing and vibration-control design absolutely essential.
✅ Effective Measures
-
Double-layer walls using soundproof + vibration-proof materials
-
“Floating floor” construction with rubber vibration-dampening panels
-
High-density acoustic absorption panels for all wall surfaces
-
Isolation design to prevent sound transmission through ceilings and floors
These techniques are used in recording studios and cinemas.
But for a creature the size of a T-Rex, they must be applied on a much larger scale.
In densely populated residential areas, even the strongest soundproofing may still be insufficient.
🧠Can a T-Rex Be Trained?
“Can’t you just train it not to growl or behave violently?”
Some may think so.
But the real issue is whether training is even possible.
Since the T-Rex is an extinct species, its behavior is not fully understood.
Assuming a resurrected T-Rex could be trained like a dog or cat, several challenges emerge:
🦴How Intelligent Was a T-Rex?
The T-Rex’s brain was relatively small for its body size.
However, it had well-developed senses—especially smell and vision—making it an excellent hunter.
-
Simple conditioned responses may be trainable
-
Routine-based behaviors tied to rewards may be learned
-
But understanding “don’t do that” and self-regulation would be difficult
In short, teaching a T-Rex not to growl or not to act out would be incredibly difficult.
🔒Safety Measures in Case of “Rampage”
A T-Rex is fundamentally carnivorous.
Even in captivity, it could panic or lash out unexpectedly.
Here are essential safety precautions👇
✅ Complete Isolation of the Living Area
-
Completely separate the T-Rex area from human living areas
-
Install reinforced steel doors and a double-door entry system
-
Equip remote-lock systems and emergency tranquilization controls
✅ Emergency Restraint & Disaster-Response Systems
-
Install a system that sprays calming gas from the ceiling when triggered
-
Prepare protocols for net guns and tranquilizer darts
-
Use noise/vibration sensors to detect abnormalities early
Only with this level of preparation does cohabitation with a T-Rex become remotely possible.
🧑🤝🧑Preventing Neighborhood Trouble Through Communication
Even with perfect facilities, you cannot eliminate anxiety or suspicion from neighbors entirely.
That’s why human communication and trust-building are essential.
✅ Hold Information Sessions for Neighbors
-
Explain the care plan, safety measures, noise levels, and emergency protocols
-
Offer periodic guided tours of the facility to reassure them
-
Provide a dedicated hotline for questions or concerns
✅ “Prevent” Complaints Before They Happen
-
Conduct monthly inspections of soundproofing/vibration systems
-
Share visualized data on noise and vibration levels
-
Prepare an immediate-response protocol for any complaints
With mutual trust, true coexistence between humans and a T-Rex becomes possible.
📝Summary|Instead of “Can It Be Trained?”, Ask “Can We Coexist?”
How do you feel after reviewing T-Rex training, noise, and safety strategies?
Here’s a recap 👇
-
T-Rex vocalizations may be low-frequency “vibration noise”
-
Traditional training is difficult—only basic conditioning may be possible
-
The living area must be fully isolated with heavy sound/vibration protection
-
Emergency tranquilization and containment systems are essential
-
Building trust and communication with neighbors is critical
Before asking “Can it be trained?”, it’s more important to ask,
“How can humans and a T-Rex safely coexist within a modern society?”
A T-Rex is not a pet you simply “raise with love.”
To live with one, system-level preparation and deep understanding are essential.
In the next chapter, we will dive deeper into the topics of healthcare, insurance, and old age.
How should we prepare for sickness, injury, or the eventual aging of a T-Rex?
We’ll explore these issues with a realistic perspective—stay tuned!
🩺Chapter 6|Medical Care, Insurance, and Old Age for a Tyrannosaurus

As our imaginary journey of keeping a T-Rex inside your home becomes increasingly realistic, we’ve explored permits, housing, feeding, waste management, and training. Now, we must face another unavoidable aspect of life: medicine and aging.
Humans and animals alike get sick and grow old.
So what about the king of dinosaurs—the Tyrannosaurus?
In this chapter, we’ll realistically examine what to do if your T-Rex gets sick and how to prepare for its “old age” as a member of your family.
🏥Does a T-Rex Even Have a “Primary Care Veterinarian”?
The first major obstacle is simple: no veterinarian on Earth is trained to treat a dinosaur.
Today’s animal hospitals typically treat👇
-
Dogs and cats (the majority)
-
Small animals (rabbits, ferrets, hamsters, etc.)
-
Some reptiles and birds
In other words, no existing vet can safely diagnose or treat a resurrected, 10-ton carnivorous dinosaur.
Even if a T-Rex were brought back through genetics, we would have zero medical data on what diseases it gets, what drugs would work, or how its body responds to treatment.
🧬A Dedicated T-Rex Medical Research Center Would Be Essential
Realistically, caring for a T-Rex’s health would require a dinosaur-specific research and medical center—not a typical pet clinic.
Facilities would need to include👇
-
Extra-large CT and X-ray equipment (for bodies over 12m long)
-
Labs that can analyze dinosaur blood, tissue, urine, and feces
-
Research teams specializing in dinosaur immunity, organs, and neurology
-
A sedation-equipped treatment room that keeps a T-Rex safely restrained
This scale of infrastructure resembles a dinosaur management facility more than a medical center.
Maintaining such a facility for even a single T-Rex could easily cost tens of millions to billions of yen per year.
💉Vaccines, Infections, and Preventive Healthcare
What diseases might a T-Rex get?
The short answer: no one knows.
We don’t know how modern viruses or bacteria affect dinosaurs—nor do we know whether ancient pathogens revived inside a T-Rex could infect humans.
Preventive measures might include👇
-
Rigorous cleaning and sterilization of the habitat
-
Immediate disposal of feces and leftover meat to prevent bacteria and insects
-
Protective suits, gloves, and masks for all handlers
-
Regular blood, urine, and stool testing
The T-Rex must be kept completely isolated from other animals to avoid cross-species infections.
🛡️Can a T-Rex Get Insurance?
A natural question is: “What if medical bills become enormous?”
Humans have health insurance. Pets have pet insurance.
But a T-Rex fits into neither category.
To insure a dinosaur, insurers would need:
-
Disease data
-
Average treatment costs and predictive models
-
Age-based risk statistics
Since none of this exists, commercial insurance is practically impossible.
In reality, all costs would need to be paid privately, or you’d need to create a dedicated self-funded insurance system.
👴T-Rex Lifespan and Senior Care
So how does a T-Rex age? What is its lifespan? Will it need nursing care?
Studies estimate that a T-Rex lived about 20–30 years.
Longer than most pets, closer to elephants or whales.
Possible signs of aging:
-
Slower movement
-
Reduced appetite
-
Muscle and bone weakness leading to falls
-
Increased susceptibility to disease
Caring for a 10-ton elderly animal requires massive space, manpower, and specialized equipment.
🛏️Designing a Comfortable Senior Life
Examples of senior-friendly T-Rex care include👇
-
Anti-slip rubber flooring to prevent falls
-
Ramps and handrail-like barriers for easier movement
-
Low-resilience mattresses to reduce bone stress
-
Crane-assisted lifting systems for when it cannot stand
-
Automated feeders and hydration systems
As it ages, changes in vocalization and bathroom habits may also require quieter surroundings and careful environmental adjustment.
⚰️When a T-Rex Dies—Handling the Final Stage
All lives eventually end—and so will your T-Rex’s.
The major issue then becomes disposal of the remains.
-
The body may weigh around 10 tons
-
Burial is impossible; cremation requires specialized high-capacity equipment
-
The government or scientific institutions may claim the remains
Alternatively, you may donate the skeleton or DNA for research—giving your T-Rex a “second life” through science.
Either way, you must be prepared to take responsibility to the very end.
📝Summary|The Final Chapter of Responsibility
In this chapter, we examined the medical care, insurance challenges, and aging of a T-Rex from a realistic perspective.
Looking back, these topics clearly cannot be handled with “cute” or “cool” feelings alone.
Let’s summarize the key points👇
-
Medical care requires dinosaur-scale facilities and research teams
-
Vaccines and infectious disease research are nearly unexplored territory
-
Insurance is unavailable—all expenses must be self-funded
-
Aging requires special environments, equipment, and nursing care
-
You must be committed to your T-Rex’s life until its very last moment
Facing the weight of life—only by truly accepting this can you say you’re ready to “own” a living creature, especially one as extraordinary as a T-Rex.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore what happens if a T-Rex faces natural disasters and emergencies: earthquakes, power outages, evacuations, and more.
Unimaginable situations demand the strongest preparation.
Stay tuned for the next installment.
🆘Chapter 7|What If a Disaster Strikes? Emergency & Disaster Preparedness for Living With a T-Rex

The idea of keeping a Tyrannosaurus indoors may sound like fantasy, yet—as we’ve explored in earlier chapters—once you seriously think it through, surprising layers of realism emerge.
However, no matter how well you prepare or how strong your facility is, there is one force humans cannot control: natural disasters.
Earthquakes, typhoons, floods, fires, power outages—
If you live with a T-Rex in a disaster-prone country like Japan, disaster preparedness becomes a matter of life and death.
In this chapter, we’ll break down how to prepare for emergencies and what actions become necessary when a disaster actually strikes—clearly and as realistically as possible.
🌪️1. If an Earthquake Strikes—What Happens to the T-Rex?
Japan is one of the most earthquake-prone countries in the world. Even earthquake-resistant buildings may suffer damage from a magnitude 7 direct quake.
So, what happens if a massive quake hits a facility where a T-Rex is housed?
Possible Risks
-
The T-Rex may panic and thrash violently
-
A 10-ton creature moving frantically can break reinforced walls
-
Falling ceilings or collapsing structures may trap or injure the T-Rex
-
If containment fails, it may escape and endanger people
During earthquakes, you must think not only about protecting yourself but also about how to secure the T-Rex safely.
🧷2. The Priority Is Not “Evacuation”—But “Containment”
In human disasters, evacuation shelters are the norm.
But evacuating with a T-Rex is impossible. (It can’t even fit through the entrance.)
This means that instead of “evacuating with the T-Rex,” the correct strategy is to securely isolate it in a safe zone.
Effective Countermeasures
-
Create a reinforced “earthquake-safe zone” within the enclosure
-
Install automatic locking and shielding systems that activate instantly
-
Prepare automated emergency food & water systems
-
Use remote monitoring cameras to track its behavior at all times
The essential policy is: Don’t move it. Don’t provoke it. Don’t let it out.
🔌3. Power Outages—Your Lifeline in Crisis
One of the most common secondary disasters is a power outage.
When the lights go out, air conditioning stops, and refrigeration, water pumps, and waste systems shut down—
Life with a T-Rex becomes extremely dangerous.
Risks During Blackouts
-
The T-Rex may panic in darkness and thrash violently
-
Loss of temperature control may cause heat/cold stress
-
Meat in freezers may rot and produce foul odors
-
Waste treatment stops, causing sanitary hazards
Backup power systems are absolutely essential.
✅ Required Backup Systems
-
Large emergency generators (diesel or solar + batteries)
-
Automatic transfer switches for instant power restoration
-
“Priority power lines” dedicated to the T-Rex enclosure
-
Stored backup food, water, and lighting for at least 72 hours
Additionally, ensure that remote monitoring and automatic control systems operate even during your absence.
💧4. Flooding & Water Damage—The Risk of “Buoyancy”
A commonly overlooked threat is flooding caused by heavy rain or rising rivers.
Even 30 cm of water can cause a creature as heavy as a T-Rex to lose footing and fall.
If water pressure damages the containment structure, escape risks increase dramatically.
Flood Preparedness
-
Build the enclosure on a raised platform (elevated floor)
-
Install drainage systems and automatic pumps
-
Add drainage channels and waterproof shutters
-
Activate “indoor lockdown mode” during heavy-rain warnings
And because wet food and waste accelerate bacterial growth, prepare waterproof equipment and cleaning procedures.
📦5. Emergency Supplies Must Be “Dinosaur-Scale”
Emergency stockpiles are essential for humans—and exponentially more important for a T-Rex.
Instead of small packaged food, you’ll need 20 kg frozen meat blocks as stock.
Minimum Required Supplies
-
Frozen meat: 30 kg × 7 days = 210 kg+
-
Drinking water: 100 L/day × 7 days
-
Cooling/heating alternatives (ice, heat packs)
-
Waste management supplies (absorption sheets, antibacterial powder)
-
Emergency restraints, sedation gas, anti-escape equipment
You’ll also need large-scale cold storage and warehouses to keep these supplies.
📡6. Coordination With Authorities & Neighbors Saves Lives
If a disaster causes the T-Rex to escape, the entire region is at risk.
This makes proactive communication and coordination essential.
Important Collaboration Points
-
Notify city offices, fire departments, and police about your T-Rex and emergency plans
-
Set up emergency communication channels (LINE, radio, etc.)
-
Explain safety guidelines to neighbors beforehand
-
Host annual “disaster drills + facility tours” to build trust
When disaster strikes, preparedness and trust save lives—whether between humans or dinosaurs.
📝Summary|Living With a T-Rex Requires Serious “Disaster Readiness”
How was this chapter?
This time, we explored the disaster-preparedness responsibilities involved in living with a T-Rex.
At this point, the question becomes not “Can you really keep one?” but rather “How much responsibility can humans carry?”
Let’s recap the key points👇
-
During earthquakes, focus on containment, not evacuation
-
Backup systems for power, refrigeration, and waste control are essential
-
Install elevated floors + drainage systems for flood safety
-
Prepare large-scale food, water, climate, and sanitation reserves
-
Coordinate proactively with the community to prepare for potential escapes
To live alongside a T-Rex, your dream must be supported by equally enormous disaster preparedness.
In the next chapter, we’ll finally explore daily life with a T-Rex—bonding, recreation, and building trust.
Not just “keeping” a dinosaur, but coexisting with one.
We’ll take you further into the reality of this imaginary life—don’t miss it.
🆘Chapter 7 | What If a Disaster Strikes? Disaster Preparedness for a Home Living With a Tyrannosaurus

The idea of keeping a Tyrannosaurus indoors may sound like pure fantasy, yet as you’ve seen throughout the previous chapters, when you think seriously about it, unexpected “realities” begin to emerge.
However, no matter how much equipment you prepare, there is one thing humans can never fully control.
That is natural disasters.
Earthquakes, typhoons, floods, fires, blackouts—
In a country like Japan where natural disasters are frequent, living with a T. rex requires a level of risk management that is truly life-or-death.
In this chapter, we’ll explore how to prepare for such emergencies,
and what actions are needed when disaster actually strikes—
explained as clearly and concretely as possible.
🌪️1. What Happens to a T. rex During an Earthquake?
Japan is one of the world’s most earthquake-prone countries.
Even the strongest buildings cannot completely withstand a magnitude-7 class direct quake.
So what would happen if a building housing a Tyrannosaurus were hit by a massive earthquake?
Possible Risks
-
The T. rex may panic and begin rampaging
-
A 10-ton body thrashing around could destroy even reinforced seismic walls
-
Falling ceilings and collapsed structures may block escape routes
-
There is a risk of escape leading to secondary damage (harm to humans)
During a quake, it’s not only about “how to protect yourself,” but also “how to safely restrain the T. rex.”
🧷2. In a Disaster, the Goal Is Not “Evacuation” but “Isolation”
For humans, the standard procedure during disasters is to evacuate to a shelter.
But bringing a Tyrannosaurus to an evacuation center… is impossible.
(It wouldn’t even fit through the entrance.)
Therefore, the strategy for a T. rex is not to “evacuate together,” but to safely isolate it in place.
Effective Measures
-
Create a “seismic-reinforced zone” inside the habitat (reinforced steel section)
-
Install systems that automatically deploy chains or soundproof shields
-
Prepare a food and water auto-supply system
-
Use remote monitoring cameras to track the T. rex
In short: “Don’t move it,” “Don’t stimulate it,” and “Don’t let it out.”
🔌3. Power Outages Become a Life-or-Death Situation
One of the most common disaster events is a blackout.
When the lights go out, air-conditioning stops, and all soundproofing, freezing, and water systems halt—
life with a T. rex instantly becomes extremely dangerous.
Dangers During a Blackout
-
The T. rex may panic in total darkness
-
Loss of climate control may cause heat or cold stress
-
Freezers stop, leading to meat spoilage and foul odors
-
Waste-processing systems fail, causing rapid sanitation issues
Therefore, blackout countermeasures are absolutely essential.
✅ Equipment Required for Blackout Readiness
-
Large emergency generator (diesel / solar + battery)
-
Automatic switch-over system for instant response
-
Prioritize power restoration for T. rex habitat only
-
Stock at least 72 hours of frozen food, water, and lighting
And to handle blackouts while you’re away, remote-controlled systems and smart alarms are highly recommended.
💧4. The Hidden “Buoyancy Risk” in Flooding
Floods and heavy rain also pose serious risks often overlooked.
Even a water depth of 30 cm can cause a massive T. rex to lose footing and fall.
Water pressure may damage facilities, increasing the risk of escape.
Flood Countermeasures
-
Build the habitat floor elevated above ground level
-
Install multiple drains and automatic pumping
-
Add gutters and waterproof shutters
-
Switch to “indoor lockdown mode” when heavy rain warnings are issued
Wet food and waste also grow bacteria quickly, so waterproof equipment and cleaning plans are a must.
📦5. Emergency Stockpiles Must Be “Mega-Scale”
Stockpiling is important for humans—but for a T. rex, the required scale is completely different.
Instead of small-packaged pet food, you need 20-kg blocks of frozen meat.
Minimum Stockpile Requirements
-
Frozen meat: 30 kg/day × 7 days = 210 kg+
-
Water: Approx. 100 liters/day × 7 days
-
Climate control: Ice / heat packs
-
Waste management: absorption sheets, gel powder, antibacterial agents
-
Restraint gas, emergency chains, escape-prevention gear
And of course, you’ll need a large cold storage facility to keep all of this.
📡6. Coordination With Neighbors Can Save Lives
If a disaster causes a T. rex to escape—
the impact extends to the entire community.
That’s why coordinating with local authorities and residents beforehand is extremely important.
Key Collaboration Points
-
Report the T. rex care plan to city hall, fire department, and police
-
Set emergency contact routes (LINE / radio)
-
Inform neighbors of evacuation rules and safe zones
-
Hold annual “disaster drill + viewing days” to build trust
“In emergencies, preparedness and trust save lives”—this holds true for both human communities and dinosaur cohabitation.
📝Summary | Living With a T. rex Requires Disaster-Readiness
How was this chapter?
In this section, we explored realistic disaster preparedness for living with a Tyrannosaurus.
At this point, the question becomes less “Can we really keep one?” and more “How much responsibility can humans take on?”
Here’s a quick recap 👇
-
During earthquakes, “isolation,” not “evacuation,” is essential
-
Backup systems for power, freezing, and waste processing are mandatory
-
For floods, use elevated floors + drainage systems
-
Stockpile one week’s worth of food, water, climate control, and sanitation
-
Coordinate with local communities to prevent escape or chaos
To make the dream of living alongside a T. rex a reality,
you must have the disaster-readiness and responsibility needed to support that dream.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore “leisure, bonding, and building trust” with a Tyrannosaurus.
Beyond simply “keeping” one—what does it mean to actually “spend life together”?
We’ll dive into the deeper reality of this imaginary coexistence, so stay tuned.
🎡Chapter 8 | Daily Life and Leisure With a Tyrannosaurus
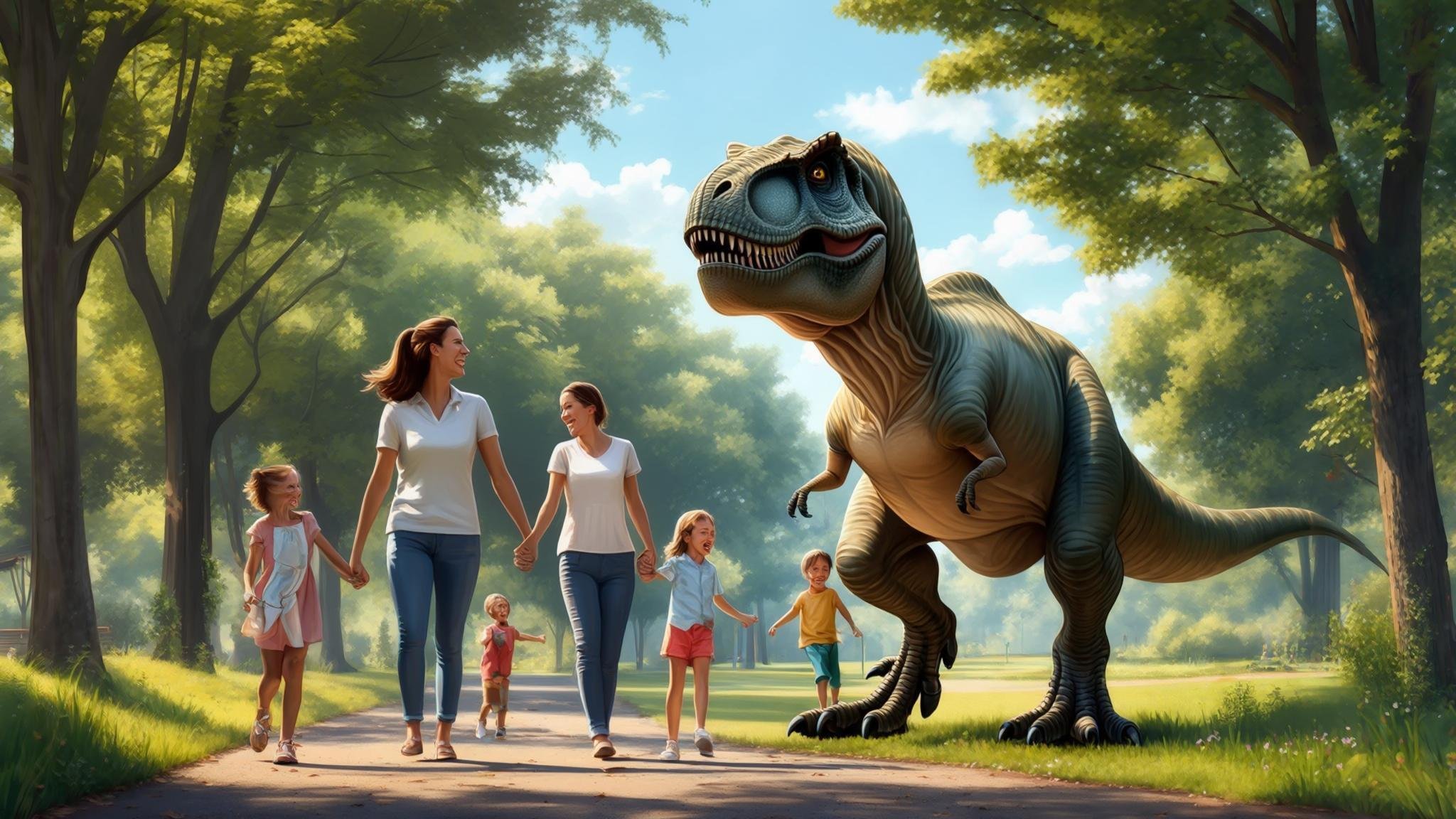
Up to this point, we’ve explored the realistic side of T. rex care—permits, living space, diet, medical needs, and disaster preparedness.
But if you’re going to live with a Tyrannosaurus, it shouldn’t be only about “keeping” one—
it’s also important to build a bond and find joy in your everyday life together.
In this chapter, we’ll imagine the “everyday life with a T. rex,” including leisure activities, communication techniques, and ways to deepen emotional connection.
🐾What Does “Quality Time” With a T. rex Look Like?
First, try to imagine this:
You wake up in the morning, and the T. rex slowly opens its eyes.
It sniffs the air with its huge nostrils, senses your presence, and lets out a rumbling call—
Just imagining that is enough to make anyone excited.
But here’s the important point: you’re not treating it like “just a pet,” but as a “partner you live with.”
Daily life with a massive, powerful, instinct-driven creature requires intentional and thoughtful interaction from the human side.
📅A Sample Daily Schedule (Morning to Night)
Let’s simulate an imaginary day together 👇
🌅Morning (7:00)
-
Open the habitat shutters and greet the T. rex with a “Good morning.”
-
Check the automatically cleaned waste area and observe health (eyes, nose, movement).
-
Breakfast: heat and cut frozen meat, place it at the feeding station.
-
“Sit time” after meals (training) and vocalization conditioning.
🕒Noon (12:00)
-
Open the skylights for indoor sunbathing (UV exposure).
-
Stimulate the brain with enrichment games (meat-search puzzle, etc.).
-
Monitor heart rate and movement via sensor during nap time.
-
Play classical/healing music to create a relaxing atmosphere.
🌇Evening (17:00)
-
Walk time (10–15 min on an indoor track or dedicated walking zone).
-
“Touch practice” before dinner (nose touches a designated pole).
-
Training success earns additional meat treats.
🌙Night (21:00)
-
Dim the habitat lights and switch to night mode (quiet, low lighting).
-
Say “Good night” using a calm voice.
-
Monitor night movement through external cameras and save recordings.
Life with a T. rex requires not only care, but also creating daily routines through meaningful interaction.
🎾How Do You Do “Leisure” With a Giant Dinosaur?
When you think of “play,” you might imagine throwing a ball with a T. rex…
Realistically, that’s impossible.
After all, a T. rex is a creature with strong hunting instincts.
But!
If you redefine “play” as exercise and enrichment, there are many activities it can enjoy.
✅Recommended T. rex Leisure Activities
-
Meat-block search game
Hide pieces of meat around the room to stimulate scent-tracking instincts.
→ Enhances concentration and satisfies natural drives. -
Fixed-rope tug-of-war
A rope anchored to the wall serves as strength training.
→ Safe if designed with proper load control. -
Water-play zone (large shallow pool)
Using reptile-like traits, cool the body and relax in chilled water.
→ Effective against heat stress. -
Vibration-speaker sound therapy
Assuming it enjoys deep bass vibrations, play low-frequency healing sounds.
→ Helps reduce anxiety and promotes relaxation.
The purpose of these activities is to use energy safely and reduce stress.
🤝How to Build Trust With a T. rex
No matter how much equipment or food you prepare—
if the T. rex doesn’t see you as “trustworthy,” coexistence becomes difficult.
So, how do you become a “trusted caretaker” in its eyes?
✅Key Points for Deepening Trust
-
Speak to it daily
→ Make gentle verbal routines like “Good morning” or “Dinner time.” -
Avoid movements that scare it
→ No sudden sounds or gestures; calmness builds trust. -
Maintain a predictable daily rhythm
→ Regular schedules help it feel “safe with you.” -
Use praise and rewards
→ Offer meat treats or gentle touches when it behaves calmly or follows directions.
A T. rex cannot speak, but it understands trust through “behavior” and “consistent daily patterns.”
📸Ideas for Viral SNS Content
If you plan to share your T. rex life on SNS or note—
aiming for “funny yet impressive” content works better than simple logs.
Here are some content ideas that might go viral 👇
-
“T. rex tries ice for the first time” challenge (observe reaction to cold air only)
-
“Ultra-low bass classical music vs T. rex” reaction comparison
-
“If a T. rex did housework” comedy photos using costume props
-
“No-meat-if-you-roar challenge” experiment series
Of course, safety would be the top priority in reality, but a mix of humor × realism × intelligence tends to resonate well online.
📝Summary | Filling Each Day With Joy
In this chapter, we explored daily life and leisure with a T. rex.
Living with a living, breathing creature brings serious responsibility—
but also plenty of joy and emotional rewards.
Let’s review the key points 👇
-
Life with a T. rex requires a balance of routine and stimulation
-
Leisure should tap into instinct-driven activities
-
Trust is built through daily communication and consistency
-
SNS/note content shines when mixing “humor × realism”
-
Even play requires safety, health, and relationship-building
Within the dream of “living with a T. rex,” there lies a mix of caretaker responsibility and irreplaceable moments.
In the next chapter, we’ll dive into the “cost and economic simulation” of living with a T. rex—how much does it cost annually, and is it realistically sustainable?
Don’t miss the next chapter!
💰Chapter 9 | How Much Does It Cost to Keep a T. rex for a Year? A Complete Breakdown of Realistic Care Expenses

“I want to keep a Tyrannosaurus indoors!”
We’ve explored this dream-like idea seriously up to this point, but now we finally need to confront a very real issue—money.
No matter how exciting the dream may be, the question of whether it’s realistically sustainable all comes down to cost.
In this chapter, we’ll simulate initial costs, monthly maintenance expenses, and the total annual amount required.
There will be many numbers, but don’t worry—we’ll explain everything in a beginner-friendly way.
By the end, you might find yourself thinking, “Could I actually afford to keep one?” So stick with me through the chapter!
💡Let’s Start With the *Initial Costs*
A Tyrannosaurus is less of a “pet” and more of a full-scale “care project.”
Because of that, the upfront costs are massive. Here are the major estimated initial expenses:
● Construction of a gymnasium-sized facility: approx. 200–300 million yen
● Floor reinforcement (10-ton load capacity): approx. 50 million yen
● Escape-prevention security system: approx. 30 million yen
● Care equipment (freezers, waste management, monitoring systems, etc.): approx. 20 million yen
● Permit acquisition and care-plan design: approx. 10 million yen
● Initial supply of frozen meat (first month): approx. 3 million yen
● Transport and introduction of the T. rex (hypothetical): approx. 50 million yen
● Insurance and legal preparation: approx. 5 million yen
▶ Total: approx. 500–600 million yen
This is no longer in the realm of “pets”—it’s on the scale of building a small zoo.
🧾How Much Are Monthly Maintenance Costs?
Once the facility is built, the next major expense is the “monthly cost of living.”
In other words, the ongoing expenses required to live with a T. rex.
● Food costs (about 900kg of meat per month): approx. 1–1.5 million yen
● Electricity (freezers, climate control, lighting): approx. 300,000–500,000 yen
● Waste disposal and sanitation: approx. 100,000 yen
● Medical and checkup fund: approx. 200,000 yen
● Staff wages (minimum 2 people): approx. 600,000–800,000 yen
● Maintenance and repairs: approx. 200,000 yen
● Insurance and property tax: approx. 100,000 yen
▶ Total: 2.5–3.5 million yen per month
This is equivalent to the operating cost of a small to mid-sized company.
That’s how expensive “serious dinosaur care” truly is.
📅So How Much Per Year?
Multiplying the monthly costs by 12 gives us the annual maintenance cost.
● 3 million yen × 12 months = approx. 36 million yen
● Including emergency and unexpected repairs: approx. 40 million yen
At this point, it’s basically “a house’s worth of money disappearing every year.”
Living with a T. rex requires truly titanic financial power.
👛How Much Is Needed in the First Year?
● Initial costs: approx. 500–600 million yen
● Annual maintenance: approx. 40 million yen
▶ Total for the first year: approx. 600 million yen
Hearing this, many people might think, “Yeah… that’s impossible.”
But that just shows how extraordinary a creature like the T. rex truly is.
🎯Is There Any Way to Cut Costs?
The numbers are enormous, but if you’re looking for ways to reduce costs, consider the following strategies:
● Shared ownership (multiple people or organizations co-managing)
● Renovating unused buildings (closed schools or warehouses)
● Buying meat directly from farms to reduce food costs
● Using AI or robots to automate care tasks and reduce labor costs
● Sharing the care journey on SNS or note to generate income
Part of the fun of imagining coexistence with a T. rex is figuring out ways to make the idea feel “somewhat realistic.”
📝Summary | The Money Needed for the “Dream” of Living With a T. rex
In this chapter, we explored the financial reality of living alongside a T. rex.
To summarize:
● Initial expenses alone: approx. 500–600 million yen
● Monthly maintenance: approx. 3 million yen
● Annual running cost: approx. 40 million yen
● First-year total: approx. 600 million yen
● Cost-reduction options include shared ownership, unused facility repurposing, and AI automation
These figures make it nearly impossible for an ordinary household, but the process of “thinking through a dream seriously” develops imagination and logical planning skills.
Isn’t it amazing that we’ve taken this fantasy so far into the realm of detail and realism?
Next time, we’ll finally reach the final chapter:
“What happens when a T. rex grows old and reaches the end of its life? And what remains afterward?”
We’ll explore the end of life and the future of this shared journey.
I’d be thrilled if you stay with me until the end of this “dream caretaker’s life.”
🕊Chapter 10 | What If Your Tyrannosaurus Reaches the End of Its Life? Facing Farewell and What Comes After

Up to this point, we’ve examined the idea of “what if you seriously kept a Tyrannosaurus indoors?” from every possible angle—permits, space, food, waste, medical care, disaster planning, daily life, and financial cost.
So then, what happens whenits life comes to an end?
In this chapter, we focus on the T. rex’s lifespan and final moments, exploring gently and carefully how to face its death—and how to move forward afterward.
To “care for a living creature” also means to take on the responsibility of facing its death.
It’s a bittersweet theme, but one that offers deep lessons and emotional insight.
🦖How Long Does a Tyrannosaurus Live?
One of the first questions that naturally comes up is its “lifespan.”
Based on comparisons with modern reptiles and large animals, we can estimate the T. rex lifespan.
Scientific projections suggest a Tyrannosaurus may live for around 30 to 40 years—slightly shorter than large mammals like lions or elephants.
If one were revived in modern times, environment, diet, and medical technology could shift this number slightly, but it is reasonable to assume a 30-year companionship when preparing to live together.
📉How Does Aging Appear?
Signs of aging in a Tyrannosaurus might include:
● Slower movement
● Reduced appetite
● Difficulty with waste elimination and temperature regulation
● Weaker vocalization
● Longer sleeping hours
● Muscle loss and sagging skin
These changes resemble the aging process of elderly humans or large senior dogs.
In other words, this is when a “caregiving phase” begins.
As the caretaker, you’ll need to observe daily health conditions and assess “how much it can still do independently” and “when assistance becomes necessary.”
🛏What Preparations Are Needed for Caregiving and End-of-Life Support?
During the T. rex’s final stage of life, you’ll face the unknown frontier of “dinosaur caregiving.”
Necessary preparations might include:
● Softer flooring materials (to reduce joint strain)
● Automated feeding with smaller, easy-to-consume cuts
● Enhanced vacuum-based waste removal for bedridden periods
● Regular massage and blood circulation care
● Recording and analyzing vocal cues for communication
● 24/7 monitoring cameras and caregiving AI
End-of-life care can sometimes be long and demanding.
To avoid overwhelming yourself, establish a team-based support system in advance.
💐When the Time Comes—How to Say Goodbye
No matter how deeply you cherish your T. rex, the day of farewell will inevitably arrive.
How you face that moment becomes a true test of your commitment.
A realistic sequence may include:
● Confirming death (no heartbeat or movement)
● Autopsy and cause-of-death analysis (in cooperation with researchers)
● Body preservation and cooling
● Considering cremation or burial (depending on local laws and sanitation rules)
● Creating a memorial space (bones, teeth, photos, records)
● Posting a tribute article or video on SNS or note
One key issue is whether cremation is even possible.
A 12-meter, 8-ton body would require a special cremation facility—or, alternatively, a large burial site the size of a soccer field.
Some owners may choose to preserve bones, teeth, or pieces of skin as memorial keepsakes.
These samples hold scientific value as well, and could even be displayed in museums.
🌱Life After Loss and the “Hole in the Heart”
After losing a pet, many caretakers experience pet loss grief.
With a creature as overwhelmingly present as a T. rex, that sorrow could be even greater.
During this time, the most important thing is to not suppress your emotions.
● Look through photos and videos to remember
● Write memorial posts on note
● Build a monument using bones or footprints
● Turn the empty facility into a museum
● Use the period to prepare emotionally for new beginnings
Tears may come at first.
But that simply proves how deeply you loved your companion.
And the days you spent with your T. rex will continue to live on inside you, becoming a priceless treasure.
📚Passing the T. rex’s Story to Future Generations
Here’s something to think about: your relationship with the T. rex doesn’t have to end as a “single lifetime memory.”
It can become a message for the future.
For example:
● Publish your caretaking records as an e-book
● Provide care data to research institutions
● Host lectures on “human–dinosaur coexistence”
● Establish a memorial fund in the T. rex’s name
Through these efforts, your story with your T. rex could become “someone’s inspiration” or “valuable research material.”
In other words, a life doesn’t end at death—it continues to live through the stories that are passed on.
📝Summary | What It Means to Be Responsible for a Life
Thank you for reading to the very end.
Though keeping a Tyrannosaurus indoors may seem absurd, at its core this theme reflects a universal truth about living alongside another life.
Here’s a summary of this chapter👇
● A T. rex’s estimated lifespan is 30–40 years
● Aging appears as changes in behavior and physical condition
● End-of-life requires caregiving and monitoring systems
● Farewell demands emotional and logistical preparation
● Even after death, its life continues through records, memorials, and sharing
We can’t actually keep a real T. rex.
But by seriously imagining the “what if,” we gain a chance to reflect on how we relate to life—and how we live our own lives.
📘Final Summary | The Unexpected Truths Revealed by Seriously Imagining an “Impossible Fantasy” of Keeping a T. rex

🦖It All Started With a Single Question.
“What if you could keep a Tyrannosaurus indoors?”
This entire content began from a single, impossible-sounding idea.
But as you read further, it transformed from a silly joke into a grand, realistic thought experiment.
Throughout the main chapters, we explored “what would actually happen if you tried to keep a T. rex” by simulating laws, structures, costs, daily life, and even end-of-life scenarios.
✅The 10 Themes Covered in This Note
-
Legal permits and regulatory barriers
-
Indoor space and required structures
-
Food quantity, cost, and procurement
-
Waste (poop) management
-
Training, noise, and neighbor issues
-
Medical care, insurance, aging, and end-of-life
-
Disaster planning (earthquakes, power outages, floods)
-
Daily life and recreation with a T. rex
-
Annual cost and economic simulation
-
Facing death and what follows
Each chapter blended “fiction × reality,” creating content that is fun to read while naturally strengthening your thinking skills, imagination, and understanding of real-world systems.
📚What This “Seriously Absurd Fantasy” Has Taught Us
Now that you’ve finished reading, you may be feeling a mix of emotions.
“Ridiculous, but entertaining.”
“Surprisingly realistic and thought-provoking.”
“Caring for a life is so deep and complex.”
“It made me reflect on my own life.”
If you felt any of these, then this content has achieved its purpose.
Because this wasn’t just entertainment—it was a mirror that uses impossible fantasy to help you reflect on your real life and your relationship with living beings.
💡Fantasy Can Become a Switch That Moves Reality
When we focus only on reality, our thinking becomes narrow without us noticing.
But when we seriously explore unrealistic fantasies, new perspectives, creativity, and bold ideas naturally arise.
Keeping a T. rex may be the ultimate “useless idea.”
But thinking about it seriously becomes a way to make your real life deeper, richer, and more enjoyable.



Comment